We present soundings data as the table of Rhoa logarithms, where each spacing corresponds to a row, and each sounding site - to a column. The effect of horizontally-layered medium in such table will be displayed simultaneously for all sites, P-effect will be displayed simultaneously on all spacings, and C-effect - as lines, inclined under angele of 45 degrees; to the left or to the right, depending on type of array and sounding technology. To this table we apply algorithm of median polishing, but in addition to rows and columns we shall also include in processing inclined lines, corresponding to C-effect. The result of algorithm operation is the decomposition of an initial field into several components, connected with: a) position of moveable (C)and unmoveable electrodes(P); b) horizontally-layered structure (HLS) and c) some rests (R).

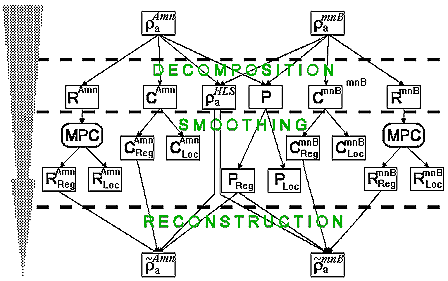 After
decomposition each component is filtered from high-frequency noise, connected
basically with near-surface inhomogeneities and errors of measurements.
Parameters of filtering (width of smoothing window) are selected by user.
At the last stage the reconstructing process is applied - the smoothed
components are united back into Rhoa field (see fig.). The values
of P- and C-effects can be estimated separately for each site of a traverse
and can be drawn as separate diagrams.
After
decomposition each component is filtered from high-frequency noise, connected
basically with near-surface inhomogeneities and errors of measurements.
Parameters of filtering (width of smoothing window) are selected by user.
At the last stage the reconstructing process is applied - the smoothed
components are united back into Rhoa field (see fig.). The values
of P- and C-effects can be estimated separately for each site of a traverse
and can be drawn as separate diagrams.
Thus, the technology of processing with the program Median in IPI-2D
package allows to reveal effects of distortions caused by near-surface
inhomogeneities and to remove them, to see effects from deep inhomogeneous
objects and to separate the influence of horizontally-layered medium. Layered
medium can be subjected to quantitative 1D interpretation. Deep objects
can be interpreted with the help of 2D forward problem account, including
both deep inhomogeneities and layered medium.